45 label the enzyme substrate and active site
Approaches to labeling and identification of active site ... - NCBI by SG Withers · 1995 · Cited by 255 — Conclusive identification of the active site residues frequently requires determination of the structure of an enzyme/inhibitor or enzyme/substrate complex. Enzyme labelling wkst HUB.doc - Enzyme Worksheet 1. On the... Enzyme Worksheet 1. On the diagrams below, label the enzyme, substrate, enzyme-substrate complex and the active site. In the box, write down what type of reaction is occurring. Catabolism Catabolism Anabolism 2. Use one of the images above to describe the "lock and key" model of enzyme activity.
Structure of Enzyme: Function, Properties, Features - Embibe Fig: Enzyme and its Active Site. 10. Allosteric sites: Apart from active sites, enzymes have allosteric sites or inhibitor sites.Inhibitors may join an enzyme at an active site or allosteric site. The binding of inhibitors to allosteric sites modifies the structure of the active site, thus preventing the binding of substrate to the enzyme.This process is called allostery or allosteric inhibition.
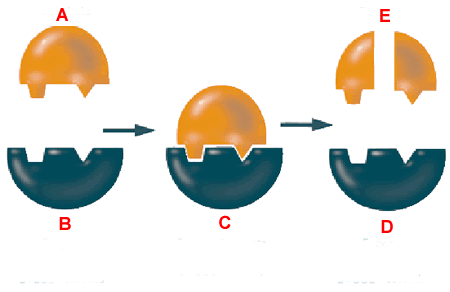
Label the enzyme substrate and active site
What is the Active Site of an Enzyme - Pediaa.Com The active site of an enzyme is the region where specific substrates bind to the enzyme, catalyzing the chemical reaction. Substrate binding site along with the catalytic site form the active site of the enzyme. The enzyme binds with a specific substrate in order to catalyze a chemical reaction that changes the substrate in some way. PDF Enzyme Diagram - Currituck County Schools Enzyme Diagram Label: Substrate, Enzyme, Active Site, Free Energy, Progress of the Reaction, Enzyme-Substrate Complex, Products Reactants, Products, With Enzyme, Enzyme substrate Diagram | Quizlet Substrate is a molecule acted upon by an enzyme products These are what a substrate is transformed into as then released from the active site Active site where a substrate bonds with an enzyme enzyme one which catalyzes chemical reactions involving a substrate enzyme-substrate complex forms when the substrate bonds with the enzyme's active site
Label the enzyme substrate and active site. Substrates, enzyme - Big Chemical Encyclopedia Substrates, enzyme Enzymes are basically specialty proteins (qv) and consist of amino acids, the exact sequence of which determines the enzyme stmcture and function. Although enzyme molecules are typically very large, most of the chemistry involving the enzyme takes place in a relatively small region known as the active site.In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, binding occurs at the active site to ... Enzyme-substrate Complex - Biology Wise In a chemical reaction, the step wherein a substrate binds to the active site of an enzyme is called an enzyme-substrate complex. The activity of an enzyme is influenced by certain aspects such as temperature, pH, co-factors, activators, and inhibitors. Enzymes are substances that play a crucial role in carrying out biochemical reactions. Enzyme-Substrate Complex | Diagram & Overview - Study.com An enzyme substrate, the substance upon which an enzyme acts, lands in the active site and is converted into an enzyme-substrate product, the substance produced as a result of the reaction. Enzymes... PDF Draw and label ACTIVE SITE, ENZYME, PRODUCT, SUBSTRATE in the diagram. enzyme activity •speeds up a reaction •by making it easier for the reaction to occur (lowering activation energy) •identify what is the enzyme, substrate, product, and the active site in your creation •enzyme must be unchanged by the reaction (reusable); substrate must be changed to a product.
Enzymes Diagram | Quizlet active site The part of an enzyme or antibody where the chemical reaction occurs substrate the substance added to an active site sucrase an enzyme that acts upon sucrose lactase enzyme that breaks down lactose lock and key enzymes in which one type of enzyme fits one type of molecule. DOCX cpb-us-e1.wpmucdn.com ENZYME BASICS PRACTICE. Lock and key model: 1. Label the diagram using the words: active site, products, enzyme, substrate. ENZYME. ENZYME-SUBSTRATE. COMPLEX. ACTIVE SITE. PRODUCT. SUBSTRATE. e._____ ENZYME FUNCTIONS: 2. Match the following words with their definitions: E ProductD Active siteB EnzymesF Catalyst. C SubstrateA Activation Energy Affinity Label - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Affinity labels are substrate analogs that react with one or more of the amino acids ... not only can it react with the active site of the target enzyme, ... Enzyme Substrate Complex: Definition & Examples - Biology Dictionary The active site is the area of the enzyme capable of forming weak bonds with the substrate. This shape change can force two or more substrate molecules together, or split individual molecules into smaller parts. Most reactions that cells use to stay alive require the actions of enzymes to happen fast enough to be useful.
Enzymes (Updated) - YouTube The Amoeba Sisters explain enzymes and how they interact with their substrates. Vocabulary covered includes active site, induced fit, coenzyme, and cofactor.... Label the enzyme, substrate, enzyme–substrate complex ... When the substrate(Urea) is present, the enzyme(Urease) breaks it down into ammonia and carbon dioxide. To catalyze the reaction urease is needed. Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Enzymes - Answer Out Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Enzymes 2. 2. Enzymes are typically which type of biomolecule? 1. In the box below, please illustrate an enzyme and substrate. Label the following key words in your illustration: enzyme, substrate, and active site. 3. Describe the effects that enzymes can have on substrates. None 1.Draw a simple diagram that shows an enzyme molecul... - Biology - Kunduz Label the enzyme, substrate, and active site. 2. 1.Draw a simple diagram that shows an enzyme molecule and a substrate molecule. Label the enzyme, substrate, and active site. 2. The rate of a certain chemical reaction is 0.25 s-1. (a) How many molecules would react in one minute? < Previous Next > Show Answer Create an account.
Active site - Wikipedia In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site ...
Lactose And Lactase Reaction Diagram The enzyme lactase present in the small intestine is essential for this reaction. Figure 1. A ball and stick model of lactose. Interpreting this diagram. During a reaction using an enzyme, the substrate enters the active site and forms an enzyme-substrate complex. • Label the active site on the lactase diagram on. Lactase is an enzyme that ...
PDF Creating Catalytic Connections with odels Teacher Key The part of the enzyme that binds the substrate to be acted on is referred to as the active site. Once the substrate is locked into the enzyme, the two green substrate pieces may be easily ... Draw and label the enzyme, products and active site after enzymatic action. 7. Although the substrate model changed in this reaction, what changes did ...
Enzymatic (HTML5) - Bioman Bio Nov 03, 2021 · Video computer games, virtual labs and activities for learning and reviewing biology content. Great for students and teachers.
[Best Answer] in the box below, please illustrate any enzymes and ... Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions. A substrate is the molecule that the enzyme acts upon and converts to product. An active site is the part of the enzyme where the substrate binds to it. Active sites contain a specific amino acid sequence and conformation which make it easy for the substrate to bind.
Enzyme Inhibitor - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Enzyme inhibition can be categorized in three types: competitive, noncompetitive, and uncompetitive. Competitive inhibition happens when a compound similar to the substrate is present and competes with the substrate for the active sites of the enzyme obstructing the access of substrate to the active site, thus slowing down the reaction. 37,38
Function of Enzymes: Substrate, Active Site & Activation Energy Enzymes are proteins that lower the activation energy of a reaction. In doing this, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction, helping it to occur faster. However, enzymes are not consumed in a...
Analyzing Graphics: Enzymes - The Biology Corner First, they label the enzyme, substrate, active site, and products. Then they view a graph showing energy changes with and without an enzyme, revealing how enzymes lower activation energy. Students also examine a graph showing the optimal pH of pepsin and lipase. Finally, a graphic illustrates how competitive inhibition and allosteric ...


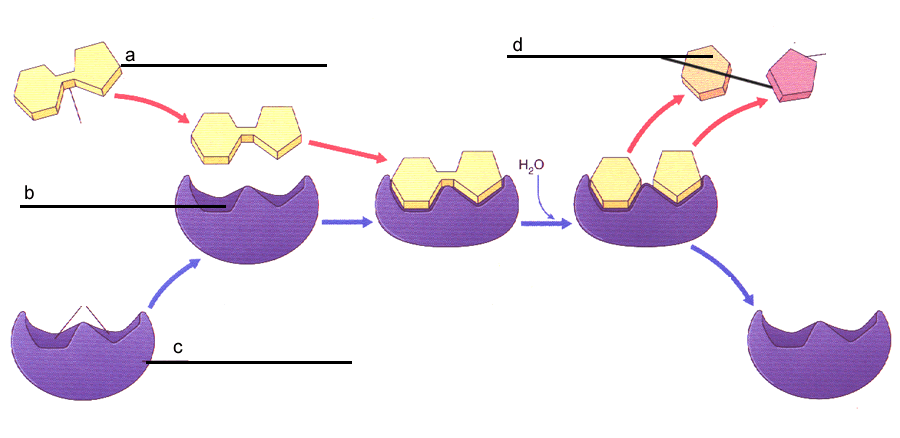
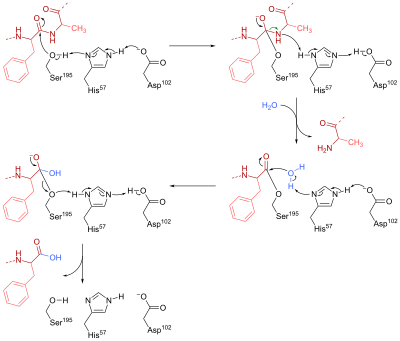
Post a Comment for "45 label the enzyme substrate and active site"